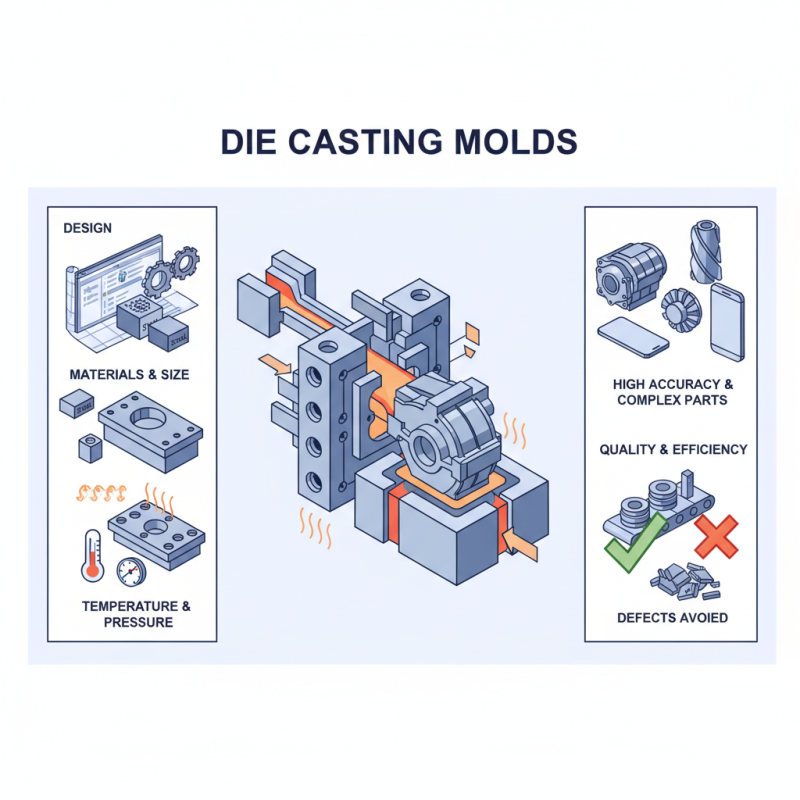
What Are Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work?
Die Casting Molds play a crucial role in manufacturing. They are essential for producing complex metal parts with high accuracy. Understanding die casting molds can enhance our grasp of the production process.
These molds are designed to form molten metal into specific shapes. They come in various materials and sizes, depending on the product requirements. The design of die casting molds is often a challenging task. Factors like temperature, pressure, and metal type impact their performance.
Improperly designed molds can lead to defects. This could waste time and resources during production. Thus, attention to detail is vital when creating die casting molds. Overall, they are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, shaping metals into high-quality components.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process that uses molten metal to create parts. This method involves forcing metal into a mold under high pressure. It is often used for large-scale production of precise and complex shapes.
The materials commonly used in die casting include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. They offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios. The process starts with heating the metal until it liquefies. Once molten, it is injected into a steel mold. The mold can be reused multiple times, which enhances efficiency.
However, the die casting process is not without challenges. Tooling costs can be high, especially for custom designs. Precision is vital, but achieving perfect shapes can be trickier than expected. Quality control is crucial. Every part must meet specifications, or it could lead to waste. Despite its potential, die casting requires continuous evaluation and improvement to ensure the best results.
What Are Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work? - What is Die Casting?
| Dimension | Description |
| Material | Aluminum, Magnesium, Zinc, Copper alloys |
| Mold Types | Single cavity, Multi-cavity, Combination molds |
| Process Steps | Melting, Injection, Cooling, Ejection |
| Applications | Automotive parts, Electronics, Hardware, Appliances |
| Benefits | High precision, Smooth surfaces, Cost-effective for large runs |
| Limitations | High initial costs, Limited to specific metals, Complex designs may incur higher costs |
Types of Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds play a crucial role in manufacturing. They are specialized tools that shape molten metal into precise forms. Various types of die casting molds cater to different needs. Each type has its unique features and applications.
One common type is the single cavity mold. This mold creates one part at a time. It is typically used for simpler designs and lower production volumes. Another type, multi-cavity molds, produces several parts simultaneously. This increases efficiency and reduces costs for mass production. Complex shapes often require hot chamber molds, which allow for fast cycle times. However, they may not be suitable for all metals.
Cold chamber molds are also popular. These molds work well with high-temperature metals. They can provide high-quality finishes but may have slower cycle times. Each type of mold has its pros and cons. Designers must carefully consider these factors to choose the right one. Not all molds are perfect. Some may lead to defects or require adjustments. It’s vital to reflect on these possibilities before committing to a specific design.
The Die Casting Process Explained
Die casting is a manufacturing process that creates precise metal components. The process involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity. This technique is favored for its efficiency and ability to produce complex shapes. According to industry reports, die casting can enhance production speed by up to 80% compared to traditional methods.
During the die casting process, the dies and molds are crucial. They must be designed for durability and precision. The typical lifespan of a die can range from 100,000 to over a million cycles, depending on the material used. Issues can arise if the mold is not properly maintained. Minor flaws can lead to significant defects in the final product, impacting overall quality.
Temperature control is also vital in die casting. Molten metal must be poured at specific temperatures to ensure proper flow and solidification. If the temperature is too high, it can cause uneven surfaces. If too low, it results in incomplete casting. As production demand increases, the need for improved die casting technology becomes essential for efficiency and precision in execution.
Materials Used in Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are crucial in manufacturing. They create high precision parts by injecting molten metal into a mold cavity. The choice of materials for these molds significantly influences the production process and the final product's quality.
Common materials for die casting molds include steel and aluminum. These materials can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Steel molds generally provide durability, while aluminum molds offer faster heat conduction, which aids in cooling times. However, aluminum molds may wear out faster under heavy use.
Tips: Choosing the right material is essential. Consider the production volume. For high volumes, invest in steel molds. For lower production runs, aluminum may suffice.
Mold design is also critical. Flaws in the design can lead to defects in the final product. Experienced designers must consider shrinkage and tolerance carefully. A slight oversight can result in significant issues during production.
Tips: Conduct thorough testing before full-scale production. Small adjustments can save time and resources in the long run. Understanding the material properties helps in making informed design choices.
Die Casting Molds: Materials and Usage
Advantages and Applications of Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds play a crucial role in manufacturing processes. Their ability to produce intricate designs with high precision is invaluable. Industries utilize these molds for their efficiency and consistency in creating complex shapes. According to a recent market report, the global die casting market is expected to reach approximately $12.5 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 5.8%. This growth illustrates the expanding demand across sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
The advantages of die casting molds are manifold. They facilitate rapid production cycles, allowing manufacturers to produce thousands of parts in a short period. Molds can be reused, which reduces material waste and costs significantly. Despite these benefits, there are challenges. The initial cost of die casting molds can be high, sometimes limiting their accessibility for small businesses. Furthermore, achieving the desired quality can require careful adjustments. If overlooked, even minor inaccuracies can lead to production delays and increased expenses.
Applications of die casting molds are diverse and wide-ranging. Automotive components, such as engine blocks and transmission cases, often rely on die casting for weight reduction and fuel efficiency improvements. Other applications extend to consumer electronics and industrial machinery, showcasing versatility. Yet, despite their extensive use, ongoing improvements in design and material are necessary to maximize their potential. This industry continually seeks innovation to enhance mold durability and casting quality.